
Worried about a surprise €4,000 VAT penalty hitting your Irish business for a single late filing? Or facing daily interest compounding on unpaid VAT that could wipe out your profits? You’re not alone thousands of businesses face these Revenue charges yearly.
This comprehensive guide covers Ireland VAT penalties 2025-2026, common pitfalls, and proven strategies to stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes.
What are VAT Penalties?
VAT penalties are financial charges imposed by Revenue Ireland for non-compliance with VAT obligations. These penalties apply to various situations including late payments, incorrect returns, and registration failures.
Revenue penalties serve as enforcement tools to ensure businesses comply with their VAT duties. The penalty system encourages timely and accurate VAT reporting across all registered businesses.
Understanding the penalty structure helps businesses make informed decisions about their VAT compliance strategies.
Types of VAT Penalties in Ireland
There are different types of VAT penalties which are stated in the below section:
Late Payment Penalties
The penalty on VAT late payment is one of the most common charges businesses face. Revenue applies these penalties when VAT payments are not made by the due date.
Penalties for late VAT payment in Ireland start at 3% of the outstanding amount if unpaid after 15 days, with an additional 3% if unpaid after 30 days. Interest accrues daily at an annual rate of about 10% after 31 days. Source : Revenue guidance on VAT penalties and interest
These rates took effect from April 2025, replacing previous lower penalty percentages.
These penalties compound over time, making early resolution essential for cost control.
Late Filing Penalties
The penalty for late filing of a VAT return in Ireland varies based on the delay period. Revenue imposes fixed penalties for returns submitted after the deadline.
Revenue Ireland adds extra charges for late filings based on how late you are:
- A 5% extra charge of the tax you owe applies if you file your return within two months after the deadline (up to a maximum of €12,695).
- A 10% extra charge applies if you file your return more than two months late (up to a maximum of €63,485). Source : Late filing surcharge rules – Revenue Ireland Tax and Duty Manual
- A standard fixed penalty of €4,000 for failure to file VAT returns on time, with additional surcharges possible for extended delays.
This extra charge is added to the total tax you owe for that time, not just penalties for being late.
Registration Penalties
Penalties for not registering for VAT apply when businesses exceed registration thresholds without registering. These penalties can be substantial and include backdated VAT charges.
Revenue may impose penalties equal to the VAT that should have been charged during the unregistered period, including a fixed €4,000 penalty for failure to register. (source)
Interest on Late VAT Payments
Interest on late payment of VAT accrues daily from the due date until full payment. The current interest rate is set by Revenue and reviewed regularly.
The rate is 0.0274% per day on unpaid VAT, applicable through 2025-2026. (source)
Interest charges apply alongside penalties, creating a double financial burden for late payments. This makes prompt payment particularly important for cash flow management.
Businesses cannot reclaim interest charges as deductible expenses, making them a pure cost to the business.
VAT Payment Penalty Structure
VAT Payment Penalty Structure
| Penalty Type | Rate | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Late Payment | 0.0219% daily interest | Applied from the due date on outstanding VAT |
| Late Filing | 5% surcharge (max €12,695) if ≤2 months late; 10% (max €63,485) if >2 months late. | Tax due based on delay period |
| Fixed Penalty | €4,000 | Standard penalty for specific breaches (e.g., failure to file a return, failure to register) |
| Non-Registration | €4,000 fixed penalty + backdated VAT | Applied if turnover exceeds registration thresholds |
| Interest | 0.0219% daily | From due date to payment |
Revenue Audit Penalties
Revenue audit penalties can be severe for businesses with compliance issues. These penalties apply when audits reveal understatement of VAT liability or other irregularities.
Audit penalties range from 3% to 100% of the additional tax due, depending on cooperation levels and disclosure quality. Businesses that make voluntary disclosures typically receive lower penalties.
The penalty calculation considers factors such as the size of the understatement, cooperation with auditors, and previous compliance history.
Key Additions for 2025 Context:
- The €6,000 Rule: Penalties are generally not sought for “innocent errors” or careless defaults where the total tax underpaid is less than €6,000.
- Publication: Details of audit settlements are typically published in the Iris Oifigiúil if the tax underpaid exceeds €50,000 (unless a qualifying disclosure was made).
How are VAT Penalties assessed?
Revenue Ireland calculates VAT penalties based on the type of mistake, the money involved, how late you are and how much you help them. Penalties change within set ranges and businesses showing good faith through telling them yourself or having a good reason may get lower penalties. The penalty check considers:
- Type and how bad the mistake is.
- Whether the mistake was done on purpose or by accident. (careless vs. deliberate behaviour).
- Past payment record.
- How fast and complete you tell them about it. (making a qualifying disclosure).
Who is eligible to appeal a VAT Penalty?
Any business that gets a VAT penalty can appeal if they think the penalty was wrong or if there is a good reasonable excuse such as being sick or unexpected computer problems.
- Appeals are made to Revenue first with proof to back up your case.
- If they say no, you can then appeal to the Tax Appeals Commission (TAC) within 30 days of the Revenue decision.
- Professional advice and documentation increase appeal success chances.
What happens when you can’t pay VAT?
What happens if I can’t pay my VAT bill is a common concern for struggling businesses. Revenue offers several options for businesses experiencing financial difficulties.
Payment arrangements allow businesses to spread VAT payments over extended periods through a Phased Payment Arrangement (PPA). These arrangements require formal application and approval from Revenue via Revenue Online Service (ROS).
Businesses should contact Revenue immediately when payment difficulties arise, as early communication often results in more favourable arrangements.
Consequences of Non-Payment
What happens if you don’t pay VAT on time includes immediate penalty charges and daily interest accumulation (currently 0.0274% per day for VAT). Revenue may also begin enforcement action for persistent non-payment.
Non payment of VAT can escalate to legal action, including referral to the sheriff, attachment of bank accounts, asset seizure, or company liquidation. These extreme measures apply when businesses ignore Revenue communications.
Early intervention prevents escalation and maintains better relationships with Revenue authorities.
How to apply for a VAT payment arrangement with Revenue Ireland?
If you can’t pay VAT on time, you can apply for a Phased Payment Arrangement (PPA) to split your payments over up to 36 months and avoid penalties.
Steps to apply:
- Log in to Revenue Online Service (ROS).
- Go to the “My Enquiries” section and select the “Payment Difficulties” category.
- Fill out and send in the ePPA1 application form with your financial details.
- You usually need to make a part payment first (often a down payment of the outstanding amount).
- Revenue reviews the applications and usually responds within 10 working days.
- Reply quickly if Revenue asks for more information to prevent delays or refusal of the arrangement.
Can You Pay VAT in Installments in Ireland?
Yes, Irish businesses can pay VAT through Phased Payment Arrangements (PPAs) or Direct Debit installments.
Key Options Available
- Phased Payment Arrangements (PPAs): For tax debts/outstanding VAT, repay over 36 months (up to 60 months with business case). Requires down-payment + monthly installments via Direct Debit.
- Direct Debit for VAT: Set monthly/quarterly payments through Revenue Online Service (ROS). First debit 3 days after approval; customizable dates.
- Annual VAT Filers: Monthly interim payments required if using Direct Debit installments.
Eligibility & Process
- Apply via ROS with PPA1 Form (for debts >€6,000 need supporting docs).
- Submit all outstanding returns first.
- Agree to full liability (tax + interest + penalties).
- Payments auto-collected; missed installments void arrangement.
Important Conditions
- Interest accrues on unpaid amounts (0.0274% daily).
- No installments for Preliminary Income Tax after Oct 31.
- VAT on advance payments must be paid with return, not installment-eligible.
Contact Revenue or your Irish accountant for personalized PPA setup.
What to expect during a Revenue VAT audit?
A Revenue VAT audit confirms correct filing and payment:
- Notification: Usually a prior notice is given, typically in writing via ROS (Revenue Online Service).
- Preparation: You provide access to your VAT records, receipts, bank statements, and relevant business papers. Records must be kept for at least 6 years.
- Review: Revenue compares your VAT returns with your backup documentation to identify discrepancies.
- Audit Report: Issues found lead to a VAT reassessment plus interest and potential penalties.
- Resolution: Discussion and settlement options are available, often involving negotiation around penalty mitigation if a qualifying disclosure is made.
- Timeline: Discussion and settlement options are available, often involving negotiation around penalty mitigation if a qualifying disclosure is made.
During an audit, businesses have the right to clear explanations, access to audit procedures, and the right to appeal penalties and assessments via the Tax Appeals Commission.
How to avoid VAT Penalties?
Here are some of the proven ways to avoid the VAT penalties:
Maintain Accurate Records
Proper record-keeping forms the foundation of VAT compliance. Businesses must maintain detailed records of all transactions, including sales, purchases, and VAT calculations.
Digital record-keeping systems help ensure accuracy and provide easy access during Revenue inspections. Cloud-based systems offer additional security and accessibility benefits.
Regular record reviews identify potential issues before they become compliance problems.
Set Up Payment Reminders
Automated payment systems prevent late VAT return Ireland situations. Electronic payment methods ensure funds transfer on time, even during busy periods.
Calendar reminders and automated alerts help businesses track important VAT deadlines. Multiple reminder systems provide backup protection against oversight.
Direct debit arrangements eliminate manual payment requirements and reduce late payment risks.
Quick Penalty Avoidance Tips
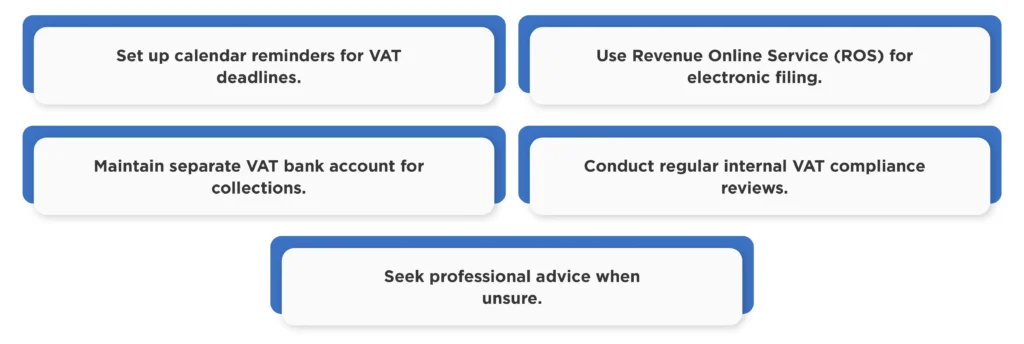
Use Professional Support
Tax advisors and accountants provide expert guidance on VAT compliance requirements. Professional support becomes particularly valuable for complex business structures or international operations.
Regular compliance reviews with professionals identify potential issues before Revenue discovers them. This proactive approach often prevents penalties entirely.
Professional representation during Revenue audits can significantly reduce penalty exposure through proper disclosure and negotiation.
VAT Payment Strategies
Below are some of the VAT payment strategies that you should keep in mind:
Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management ensures VAT funds remain available when payments fall due. Separate VAT accounts prevent mixing of VAT funds with operating capital.
Regular cash flow forecasting helps businesses anticipate VAT payment requirements. This planning prevents unexpected cash shortages during payment periods.
Businesses should treat VAT as a liability from the moment it’s charged, not as revenue available for operations.
Early Payment Benefits
While Revenue doesn’t offer early payment discounts, paying VAT ahead of schedule provides cash flow certainty. Early payment also demonstrates good compliance intentions during audits.
Early payments protect against bank processing delays that could result in technical late payments. This buffer provides peace of mind during busy periods.
Some businesses find monthly VAT provisioning easier than quarterly lump sums.
Penalty Reduction and Appeals
Here are some of the scenarios where penalty imposed can be reduced and you can appeal:
Reasonable Excuse Defence
Revenue may reduce or waive penalties when businesses demonstrate reasonable excuse for non-compliance. Acceptable excuses include serious illness, system failures, or other circumstances beyond business control.
Documentation supporting reasonable excuse claims strengthens penalty appeals. Medical certificates, technical reports, and other evidence support these claims.
Businesses must demonstrate they took all reasonable steps to comply despite the circumstances.
Voluntary Disclosure Benefits
Voluntary disclosure of VAT errors often results in reduced penalties compared to Revenue discoveries. Businesses that proactively identify and correct errors receive favourable treatment.
Complete voluntary disclosures, including full payment of outstanding amounts, typically receive the lowest penalty rates. Partial disclosures or delayed payments may not qualify for maximum reductions.
Professional advice helps ensure voluntary disclosures meet Revenue requirements for penalty reduction.
Common VAT Penalty Scenarios
Here are some of the common VAT penalty scenarios for better understanding:
Scenario 1: Late VAT Return Filing
A small business files their quarterly VAT return two weeks late due to staff illness. The penalty for late tax return Ireland would be a fixed penalty of €4,000, plus any interest on late payment.
This scenario demonstrates that even minor delays can result in a significant fixed penalty, emphasising the importance of backup procedures.
Even small penalties should be avoided as they indicate compliance weaknesses to Revenue.
Scenario 2: Incorrect VAT Calculation
A business discovers they’ve been applying wrong VAT rates for six months, resulting in VAT underpayment. Revenue audit penalties could apply unless the business makes voluntary disclosure.
Quick voluntary disclosure and full payment typically results in 10-20% penalties rather than the 75-100% penalties for Revenue discoveries.
This scenario shows the value of regular compliance reviews to catch errors early.
Scenario 3: Missed Registration Deadline
A growing business exceeds VAT registration thresholds (€85,000 for goods or €42,500 for services) but continues trading without registration for three months. Penalties include backdated VAT plus non-registration penalties of €4,000.
The total penalty could exceed the original VAT liability, making threshold monitoring crucial for growing businesses. Early registration, even before reaching thresholds, eliminates this risk entirely.
Monthly VAT Compliance Checklist
| Task | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Record all transactions | Daily | Maintain accurate VAT records |
| Review VAT calculations | Weekly | Identify errors early |
| Check payment deadlines | Monthly | Prevent late payment penalties |
| Reconcile VAT accounts | Monthly | Ensure accuracy |
| Monitor registration thresholds | Monthly | Prevent registration penalties |
Technology Solutions for VAT Compliance
Modern accounting software automates VAT calculations and reduces manual errors. Integration with bank accounts enables automatic payment scheduling.
Cloud-based solutions provide real-time access to VAT information from anywhere. This accessibility helps maintain compliance even during travel or remote work.
Software audit trails provide Revenue with clear transaction histories during inspections.
Mobile VAT Management
Mobile apps allow businesses to track VAT obligations while away from the office. Photo receipts and instant data entry prevent information loss.
Mobile solutions particularly benefit field-based businesses that collect VAT-applicable transactions throughout the day.
Integration between mobile and desktop systems ensures seamless data flow.
International VAT Considerations
Irish businesses trading internationally face complex VAT obligations that increase penalty risks. Different EU countries have varying VAT rules and rates.
Brexit has complicated UK-Ireland trade relationships, creating new compliance requirements. Businesses must understand both Irish and destination country VAT rules.
Professional advice becomes essential for international operations due to complexity.
Digital Services VAT
Online businesses selling digital services face special VAT obligations under EU rules. These obligations include registration and payment in multiple EU countries.
Non-compliance with digital services VAT can result in penalties across multiple jurisdictions. The OSS (One Stop Shop) system simplifies compliance but requires careful management.
Regular updates to digital VAT rules require ongoing compliance monitoring.
Revenue’s Penalty Mitigation Approach
Revenue Ireland has adopted a more collaborative approach to penalty management in recent years. This approach emphasises education and support over purely punitive measures.
Businesses demonstrating genuine efforts to comply often receive reduced penalties. Good compliance history and proactive communication influence penalty decisions.
Revenue’s published guidance provides clear expectations for penalty mitigation circumstances.
Compliance Improvement
Businesses with penalty history can demonstrate improvement through enhanced compliance procedures. Documentation of improved systems supports future penalty appeals.
Regular compliance reviews and professional support demonstrate commitment to improvement. This commitment influences Revenue’s approach to future compliance issues.
Investment in compliance systems often pays for itself through avoided penalties.
Conclusion
Understanding VAT penalties in Ireland requires comprehensive knowledge of Revenue requirements and proactive compliance management. Businesses that invest in proper systems and professional support typically avoid penalty exposure entirely.
The cost of compliance is invariably lower than the cost of non-compliance when penalties and interest are considered. Early intervention and professional guidance provide the best protection against Revenue penalties.
Maintaining good relationships with Revenue through transparent communication and prompt compliance creates long-term benefits for business operations.
Regular compliance reviews and system updates ensure ongoing protection against changing regulations and requirements. This proactive approach transforms VAT compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage through superior cash flow management and reduced regulatory risk.
Contact us today via call +353 212069255 or mail at info@outbooks.com.
FAQs about VAT Penalties in Ireland
What is the current VAT late payment penalty rate in Ireland?
How long do I have to file my VAT return in Ireland?
Can you delay VAT payment in Ireland?
What happens if you don’t pay VAT?
How do VAT penalties work in Ireland?
Can VAT penalties be removed or reduced?
What constitutes a reasonable excuse for VAT penalties?
How much interest is charged on unpaid VAT?
When must I register for VAT in Ireland?
What records must I keep for VAT compliance?
Parul is a content specialist with expertise in accounting and bookkeeping. Her writing covers a wide range of accounting topics such as payroll, financial reporting and more. Her content is well-researched and she has a strong understanding of accounting terms and industry-specific terminologies. As a subject matter expert, she simplifies complex concepts into clear, practical insights, helping businesses with accurate tips and solutions to make informed decisions.






